Vue2学习笔记:第十一章
- 一、脚手架配置代理
- 1.引出问题
- 2.方式一
- 3.方式二
- 二、github案例
- 1.App.vue
- 2.搜索部分Search.vue
- 3.显示数据部分List.vue
- 4.vue-resource
- 三、插槽
- 1.默认插槽
- 2.具名插槽
- 3.作用域插槽
一、脚手架配置代理
先在脚手架文件目录下npm i axios安装一下子axios
1.引出问题
跨域就是违反同源策略,同源策略就是协议、域名、端口号三个必须完全一样
解决跨域请求数据问题,要么让后端加上那个Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*',要么用jsonp的script的src属性,但这两种用的不多,我们还有第三种方式,那就是借助一个代理服务器,其端口号和请求端口号一致(这里以8080举例)
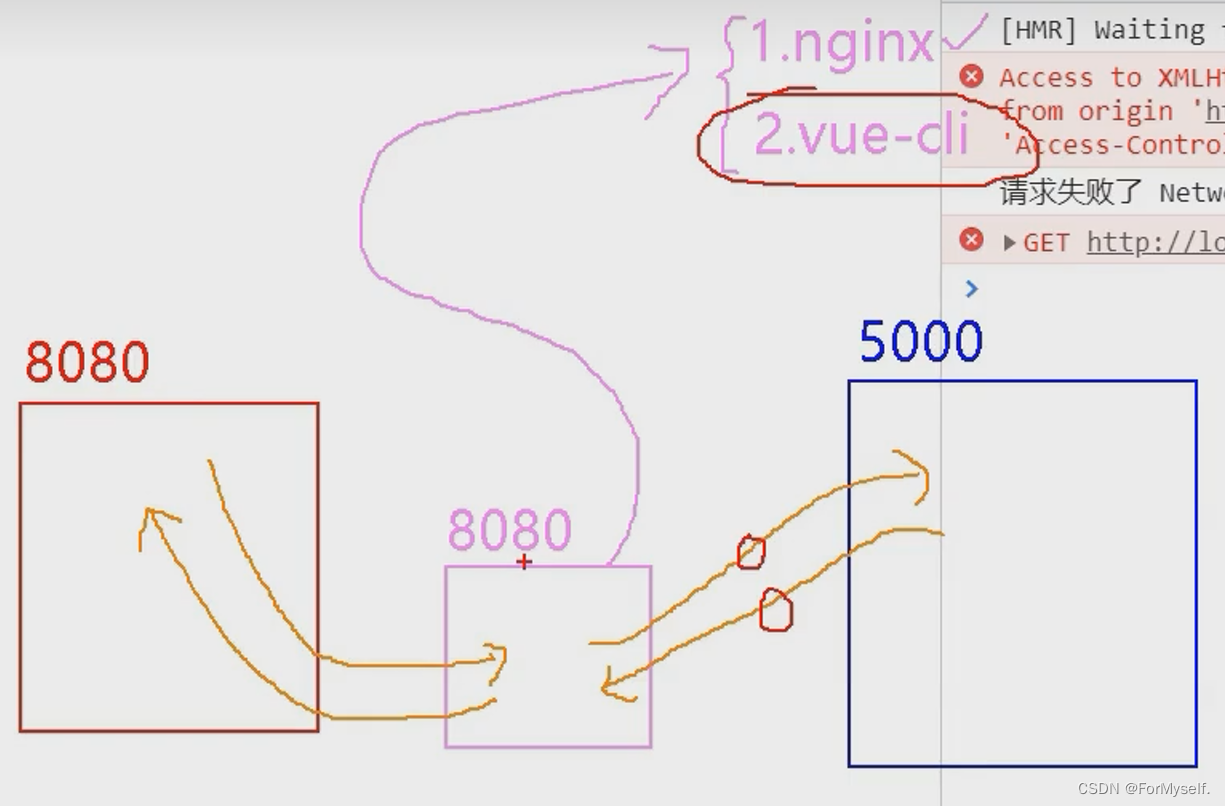
如下图,url为http://localhost:8080的前端应用要请求http://localhost:5000服务器的数据,这属于跨域请求,咋办?
可以利用vue-cli搞一个中间的代理服务器,其url也是http://localhost:8080(vue项目服务器和代理服务器是一台服务器8080),代理服务器8080和5000服务器之间交换数据不需要遵循同源策略,所以可以8080服务器可以把8080前端应用的请求转发给5000端口服务器(这地方有点晕……)
2.方式一
在vue.config.js中添加如下配置:
devServer:{proxy:"http://localhost:5000"
}
使用:
getStudents() {axios.get('http://localhost:8080/students').then(response => {console.log('请求成功了', response.data);},error => {console.log('请求失败', error.message);});
}
说明:
1、优点:配置简单,请求资源时直接发给前端(8080)即可。
2、缺点:不能配置多个代理,不能灵活的控制请求是否走代理。
3、工作方式:若按照上述配置代理,当请求了前端不存在的资源时,那么该请求会转发给服务器 (优先匹配前端资源)。这话的意思就是说,如果8080本身就有students这个路径(比如我在脚手架文件的public里新建了个students),那么请求会先找8080的这个students,如果8080没有students,才会把请求转发给5000端口去拿5000的students
3.方式二
编写vue.config.js配置具体代理规则:
devServer: {//方式二可以加路径前缀,如果看到前缀就去请求5000,不会再从8080找数据proxy: {'/zzy': {//告诉特ajax请求要转发给谁 target: 'http://localhost:5000',//pathRewrite把请求转发给5000时去掉zzy路径//一般来说后端都会写成api/xxx,就不用手pathRewrite了pathRewrite: { '^/zzy': '' },ws: true, //用于支持websocket//changeOrigin用于控制请求头中的host值// true就是把请求源改成和目标服务器一致(5000),false就是8080changeOrigin: true //写true比较合适,默认也是true(React里默认false)},'/ht': {target: 'http://localhost:5001',pathRewrite: { '^/ht': '' },}}}/*changeOrigin设置为true时,服务器收到的请求头中的host为:localhost:5000changeOrigin设置为false时,服务器收到的请求头中的host为:localhost:8080changeOrigin默认值为true
*/
使用:
getStudents() {axios.get('http://localhost:8080/zzy/students').then(response => {console.log('请求成功了', response.data);},error => {console.log('请求失败', error.message);});},getCars() {axios.get('http://localhost:8080/ht/cars').then(response => {console.log('请求成功了', response.data);},error => {console.log('请求失败', error.message);})}
说明:
1、优点:可以配置多个代理,且可以灵活的控制请求是否走代理。
2、缺点:配置略微繁琐,请求资源时必须加前缀。
3、如果8080里有zzy/students,那么还是会找8080里的文件,如果没有就发送给5000,不过一般来说是没有的,所以就发给5000然后再pathRewrite把zzy去掉就欧了
二、github案例
从https://api.github.com/search/users?q=xxx请求数据过来,然后点击搜索按钮可以显示所有github用户,咋做呢?
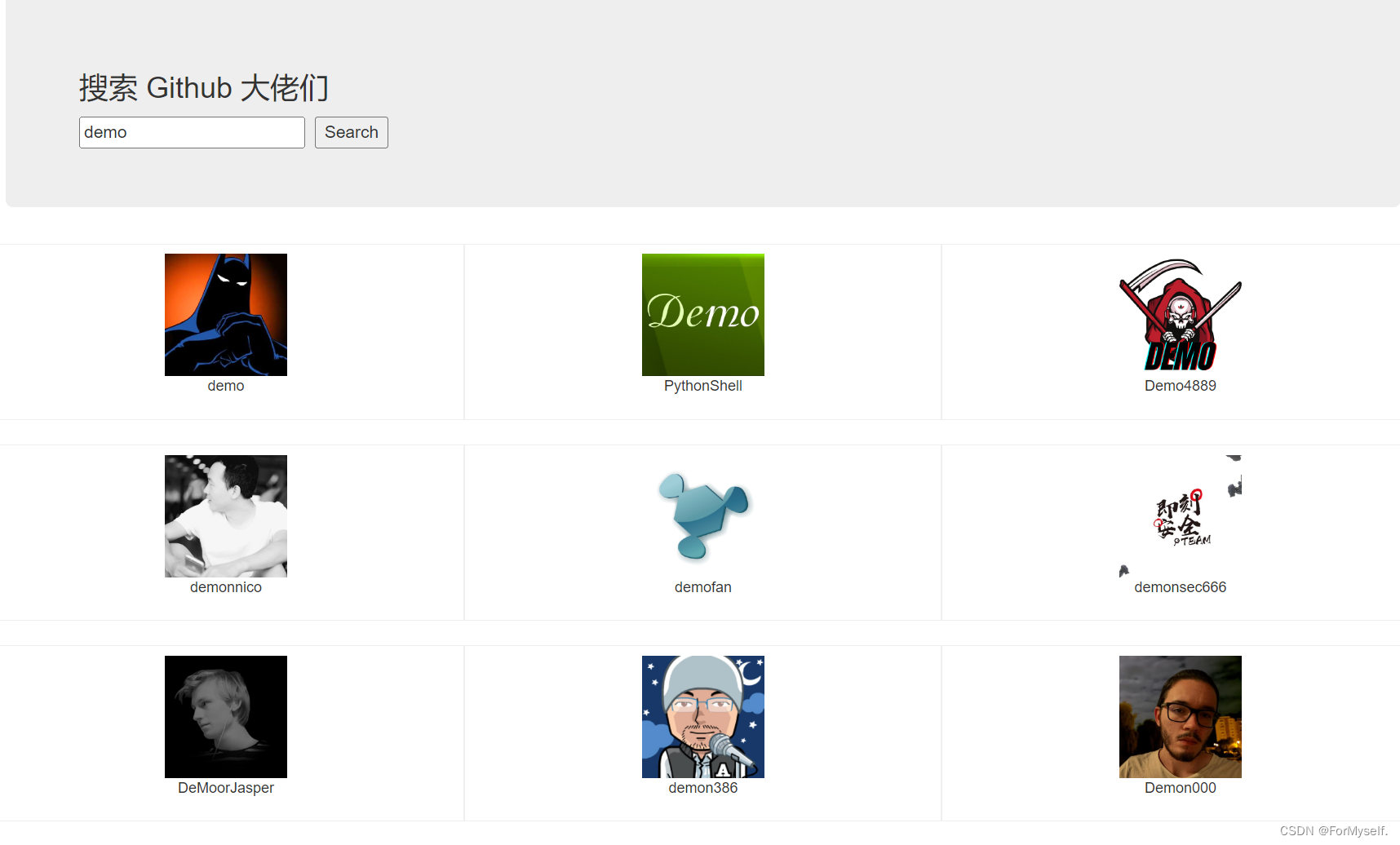
1、首先拆分html和css,这块儿直接用现成的,需要注意的是bootstrap样式需要在public下新建css文件夹粘贴bootstrap.css,然后去index.html引入,直接import会有问题
2、使用全局事件总线把请求的数据给List并使用v-for展示到页面
3、这里如果再完善一点,一上来显示欢迎词,发请求前显示loading,请求发送完若成功显示数据,失败则显示失败信息。这样的话在传数据时就要在不同的事件节点去触发全局事件并且传不同的值,比较好的做法是数据配置到对象里,传值也传一个对象,这样写起来比较方便。各个文件如下:
1.App.vue
<template><div class="container"><Search></Search><List></List></div>
</template><script>
import Search from './components/Search.vue';
import List from './components/List.vue';export default {name: "App",components: { Search, List }
}
</script>
2.搜索部分Search.vue
<template><section class="jumbotron"><h3 class="jumbotron-heading">搜索 Github 大佬们</h3><div><input type="text" placeholder="enter the name you search" v-model="keyWord" /> <button @click="searchUsers">Search</button></div></section>
</template><script>
import axios from 'axios';
export default {name: 'Search',data() {return {keyWord: ''}},methods: {searchUsers() {// 发送请求前的页面,显示Loading...// this.$bus.$emit('updateListData', [], false, true, '');this.$bus.$emit('updateListData', { users: [], isFirst: false, isLoading: true, errorMsg: '' });axios.get(`https://api.github.com/search/users?q=${this.keyWord}`).then(response => {console.log('请求成功!!', response.data.items);//请求成功的页面// this.$bus.$emit('updateListData', response.data.items, false, false, '');this.$bus.$emit('updateListData', { users: response.data.items, isFirst: false, isLoading: false, errorMsg: '' });},error => {console.log('请求失败...', error.message);// 请求失败的页面// this.$bus.$emit('updateListData', [], false, false, '请求失败啦');this.$bus.$emit('updateListData', { users: [], isFirst: false, isLoading: false, errorMsg: '请求失败啦' });//})}},
};
</script><style scoped>
/* 这里的样式用的都是bootstrap里的 */
</style>
3.显示数据部分List.vue
<template><div class="row"><!-- 展示用户列表 --><div class="card" v-show="info.users.length" v-for="user in info.users" :key="user.id"><a :href="user.html_url" target="_blank"><img :src="user.avatar_url" style='width: 100px' /></a><p class="card-text">{{ user.login }}</p></div><!-- 展示欢迎词 --><h1 v-show="info.isFirst">欢迎来到Github!</h1><!-- 展示加载中 --><h1 v-show="info.isLoading">加载中,Loading......</h1><!-- 展示错误信息 --><h1 v-show="info.errorMsg">{{ info.errorMsg }}</h1></div>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'List',data() {return {info: {isFirst: true,isLoading: false,errorMsg: '',users: []}};},methods: {//可以一个一个传,但是麻烦啊// getUsers(users, ...list) {// this.users = users;// this.isFirst = list[0];// this.isLoading = list[1];// this.errorMsg = list[2];// }getUsers(dataObj) {this.info = { ...this.info, ...dataObj }; //ES6语法,原来有的不动,重名的以后边为主// this.info = dataObj; //或者直接整个替换,但是要保证原来写的数据再写一遍}},mounted() {this.$bus.$on('updateListData', this.getUsers);}
};
</script>
4.vue-resource
在vue1.0时这个用的比较多,但是现在用axios比较多了,这个了解下就行,其实这玩意儿和axios很像,就把axios.get换成this.$http.get,其他的都一样
安装vue-resource :npm i vue-resource
引入插件:import vueResource from 'vue-resource'
使用插件:Vue.use(vueResource)
案例:
this.$http.get('http://localhost:8081/api2/cars').then(response => {console.log('请求成功了',response.data)},error => {console.log('请求失败了',error.message)}
三、插槽
1、作用:让父组件可以向子组件指定位置插入html结构,也是一种组件间通信的方式,适用于 父组件 ===> 子组件 。
2、分类:默认插槽、具名插槽、作用域插槽
1.默认插槽
比如有那么一天,我们要在页面显示三个类别,每个类别下面有不同的文字,本来是我们把数据传给子组件然后使用v-for遍历生成的文字信息,但是产品经理突然让你把美食类的下面换成图片,电影类下面换成视频,怎么搞?

有个非常好用的方法就是插槽,也就是使用slot标签在子组件挖个坑,然后在父组件的vc标签里面写东西往里边填
子组件Category:
<template><div class="category"><h3>{{ title }}类</h3><ul><slot>我是一个插槽,当使用者没有传递具体结构时,我会出现</slot></ul></div>
</template>
父组件App:
<template><div class="container"><Category title="美食"><!--往slot插入东西--><img src="http://s3.ax1x.com/2021/01/16/srJlq0.jpg" alt=""></Category><Category title="游戏"><!--往slot插入东西--><li v-for="(game, index) in games" :key="index">{{ game }}</li></Category><Category title="电影"><!--往slot插入东西--><video controls src="http://clips.vorwaerts-gmbh.de/big_buck.bunny.mp4"></video></Category></div>
</template><script>
import Category from './components/Category.vue';export default {name: "App",components: { Category },data() {return {//foods: ['火锅', '烧烤', '小龙虾', '牛排'],games: ['战神4', '极品飞车', '鬼泣', '超级玛丽'],// films: ['《教父》', '《复仇者联盟》', '《绿皮书》', '《阿甘》']}},
}
</script>
2.具名插槽
子组件使用name属性起个名,父组件理使用slot="名字"找到对应的坑位
父组件中:<template><div><Category><div slot="center">中间的结构</div><a slot="center" href="http://www.zzy.com">中间的结构</a><template v-slot:footer> 最新写法,要配合template使用<div>底部的结构</div><h4>欢迎你</h4></template></Category></div></template>子组件中:<template><div><!-- 定义插槽 --><slot name="center">插槽默认内容...</slot><slot name="footer">插槽默认内容...</slot></div></template>
3.作用域插槽
有一天,产品经理让你把每个部分的数据换个形式,换成下边这样,咋整?

这里就用到了作用域插槽,如果数据不在App中了,而在Category.vue中,然后App.vue要用到数据,这时我们就可以在Category.vue中使用slot标签给父组件App传值,写法很像当时父给子传值的props写法,在标签里搞个:games="games",然后用到插槽的地方必须使用template标签包裹,并且配置scope属性来接收数据,接过来的是一个对象
其实这个功能使用默认插槽完全可以实现,但是默认插槽是指数据在使用插槽的文件里的,那么如果数据在别的地方(比如本案例的Category.vue文件),就得用作用域插槽
Category.vue文件
<template><div class="category"><h3>{{ title }}类</h3><slot :games="games">默认内容</slot></div>
</template><script>
export default {name: 'Category',props: ['title'],data() {return {games: ['战神4', '极品飞车', '鬼泣', '超级玛丽']}},
};
</script>
注意下面第二个标签用了个解构赋值,因为传过来的是一个属性名为games的对象,解构赋值{games}相当于let {games: games} = {'games' : [数据] },这样直接用games就相当于直接用[数据]。第三个标签就相当于重命名一下
App.vue文件
<template><div class="container"><Category title="游戏"><template scope="youxis"><!-- {{ youxis.games }} --><!-- { "games": [ "战神4", "极品飞车", "鬼泣", "超级玛丽" ] } --><ul><li v-for="(game, index) in youxis.games" :key="index">{{ game }}</li></ul></template></Category><Category title="游戏"><template scope="{games}"><ol><li v-for="(game, index) in games" :key="index">{{ game }}</li></ol></template></Category><Category title="游戏"><template slot-scope="{games: youxis}"><h4 v-for="(game, index) in youxis" :key="index">{{ game }}</h4></template></Category></div>
</template><script>
import Category from './components/Category.vue';
export default {name: "App",components: { Category },
}
</script>